Power of Spinoffs: Guide to Understanding, Executing, and Successful Strategies
Spinoffs are a unique form of corporate restructuring in which a business unit is detached from its parent company and established as an independent legal entity. With the right degree of strategizing, spinoffs can benefit both the parent company and its spinoff subsidiary involved in terms of growth prospects, increased focus, improved valuations, etc.
This guide offers an understanding for this approach by introducing readers to various facets of spinoff strategy execution.
It begins with defining what constitutes a spinoff and dives into assessing the associated key risks & challenges before validating significant potential benefits across industries through detailed case studies and examples.
Contents
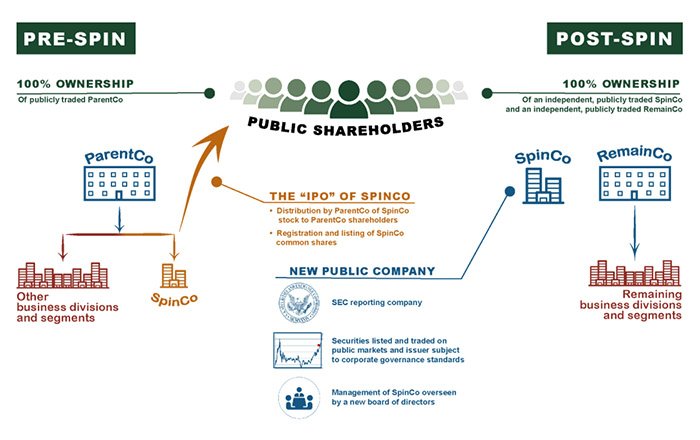
Understanding Spinoffs
A spinoff is a transaction strategy where a specific business unit or division of an established company splits off into a new, independent company with the existing parent firm keeping equity control. It enables companies to concentrate on core operations and hone their focus to overreaching organizational objectives.
The purpose of spinoffs is usually centered around shareholder value creation by separating out existing units within one enterprise, frequently along product divisions when the unit’s good fit that way. Benefits can also be unlocked for acquired firms who join forces as subsidiaries of larger corporations, partners, etc.
Different types of spinoffs
There are several different types of spinoffs, each appropriate for specific situations. Companies can create subsidiaries in which a parent firm will transfer certain components or brands to make them more operationally efficient.
They may partake in carve-outs and partial spins that usually involve the sale of business units rather than full divestment. Or they could turn to illiquidity finance which is a combination of traditional debt financing and spinoff activity.
A less common method of executing spinoffs (though one growing rapidly in recent years) is stappling splits whereby company equity holders acquire their own publicly controlling stake in a newly formed company research centrifuge upon splitting off from an originating firm.
Factors driving spinoff decisions
The decision to spinoff a business can be motivated by many different factors, ranging from financial considerations such as improved capital structure or profitability, through to operational motivations such as having spinoffs better focus on specific core areas while creating sharing economies.
A well-structured spinoff offers increased dynamic growth potential and competitive strength to both parent companies and their associated subsidiaries.
Moreover, spinning off units can lead to strategic collaborations with subsidiaries that provide benefits such as proximity of employees or specialization in a particular industry segment.
Identifying these factors is essential for companies looking go evaluate the viability of structural options involving potentially meaningful financial upside for both investors and executives.
Process of Executing a Spinoff
Identifying a potential spinoff opportunity
Identifying a potential spinoff opportunity involves evaluating strategic, financial, operational and legal considerations.
Companies typically look at how a proposed spinoff could benefit their longer-term objectives, the relevance of that business to their overall strategy, projected sources of competitive advantage through spinning off divisions or operations, projected positive effects on profitability and shareholder value as well as synergies derived from such decisions in order to determine if it makes sense.
Additionally, the resources available for executing and sustaining background preparations will need to be assessed thoroughly.
Assessing the feasibility and viability of a spinoff
Assessing the feasibility and viability of a spinoff is an important step in the process of executing a spinoff, as it helps determine whether pursuing a transaction will be beneficial for all parties involved.
In order to assess whether a spinoff presents proposed benefits that outweigh potential risks, multiple factors need to be considered such as corporate objectives, investor reactions, taxation implications etc.
Along with these considerations economic forecasts must be analyzed eliminating unwanted business activities before making the final decision on executing this type of major strategic move without any unforeseen hindrances.
Legal and regulatory considerations
Executing a successful spinoff requires a detailed assessment of various legal and regulatory considerations. Companies often must comply with both local and international regulations.
These vary widely from country to country and industry-to-industry, so it’s important to consult experts that have direct experience handling any underlying jurisdictional laws, securities rules, corporate governance issues, intellectual property matters, or antitrust topics.
Furthermore, interested parties should consider wider implications on taxes when structuring a spinoff transaction since significant adverse tax consequences can arise in certain scenarios when not structured properly.
Planning and structuring the spinoff
Planning and structuring a spinoff should include analyzing the new company structure of the target spun-off entity, evaluating regulatory compliance issues, determining any applicable tax consequences¬, creating procedures for employee risk management and relocation if necessary¬, setting up cash flows and agreements for revenue streams, formulating financing strategies and projecting future financial performance.
It is important to properly assess risks associated with forming new entities based on particularly legal considerations so as not to violate associated laws in related jurisdictions in which operations may extend. Ultimately understanding margins to be had here will enable better capital planning.
Preparing for the spinoff transaction
Preparing for the spinoff transaction involves carrying out a number of steps to ensure that all legal, regulatory, financial and administrative requirements are followed before bringing it before shareholders for a vote.
It includes filing applications and approval or waiver requests with internal committees as well as relevant governmental bodies; preparing required documents such as information memos, securities registration statements etc.;while also creating guardrails to ensure effective implementation of plans by non-management teams.
Preparing a thorough due diligence report which describes potential risks associated with the spinoff plus resources necessary for its successful completion is an essential pre-requisite prior commencement of any offers/ trades related to this transaction.
Post-spinoff activities and challenges
The post-spinoff activities are critical for the success of a spinoff transaction. They involve managing the relationship between two entities after the separation, integrating dissimilar systems and data processes and consolidating support services arrangements.
Further, it is important to identify potential risks associated with transferring resources financially and technically to ensure that appropriate measures are in place to protect both companies legally, commercially, operationally, licensingly and contractually.
Finally, maintaining communication channels open between two donor companies in order to outline expectations going forward is key during these post-spinoff periods.
Spinoff Strategies in Different Industries
Spinoffs in technology sector
Spinoffs in the technology industry present enormous business opportunities as well as leway to achieve strategic objectives such as divestitures and product segmentation. Examples of spinoff’s by some large tech firms where include PayPal, Apple Computer and Yahoo!
By forming independent entities with common backgrounds, these companies allowed for a better focus on respective services while protecting their innovations and market channels from potential disruptions or lack of investments.
Prospective technology entrepreneurs should create partnerships that integrate differing qualities to construct firm advantage points within existing competencies form enhanced diversification prospects.
Spinoffs in finance and banking sector
In finance and banking, spinoffs may be used to unlock a company’s potential value that has become hidden or sunk in their overall financial portfolio.
Examples include splitting out investment leads looking for investors to reach different objectives such as transitioning core service s offering providing sector-focused technology solutions, splitting venture capital initiatives for clearer risk ownership etc.
These strategies help in liberalizing capital efficiency of portfolios allowing involved management teams to manage fully focused businesses more efficiently than before; hence, greater valuations through accelerated growth take place when a given segment concentrates on its core business areas.
Spinoffs in consumer goods industry
The consumer goods industry is a popular target of spinoffs. Consumer goods brands spin out either to enable more entrepreneurial exploration, or when parent companies are divested.
It also reduces fixed costs associated with increased regulation and enables the freed parts to create a unique identity offering opportunities for revenue, growth, and innovation efficiently collected in data streams other areas don’t have access to.
Spinoffs allow investments into more specialized branches which promotes not only sector-specific development but market consolidation as well. Fair value measurements make sales efficient while capital reallocation better benefits shareholders in owner equity transfers during post-spinoff cost allocation processes making the process easier for general stake holders alike.
Spinoffs in healthcare and pharmaceutical sector
Spinoffs in the healthcare and pharmaceutical sector can create new business opportunities that improve drug accessibility and allow companies to develop groundbreaking products within new commercial models.
Pharmaceutical giants are utilizing spinoff strategies to monetize long-term research or acquisitions process outside of their core operations, enable exclusive specialty laboratories, and possibly limit competition borrowing from their experience.
Additionally, regulatory incentives make it financially attractive for these large companies divide up a business operation into multiple discrete units with each concentrating on its own technologies, product offerings, professional staffs and investors.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Identifying and mitigating risks associated with spinoffs
The success of a spinoff can depend on properly identifying and mitigating the associated risks. Such risks can have an adverse effect on the parent company as well as its spinoff.
These include leadership risk, market risk, capital structure risk, tax and regulatory issues, operational risk of failing to establish separate structures, etc.
It’s important for companies seeking to execute a spinoff strategy to ensure that these potential hazards are identified and best practices established around assessing them & developing mitigation plans accordingly.
Challenges in managing the transition and separation process
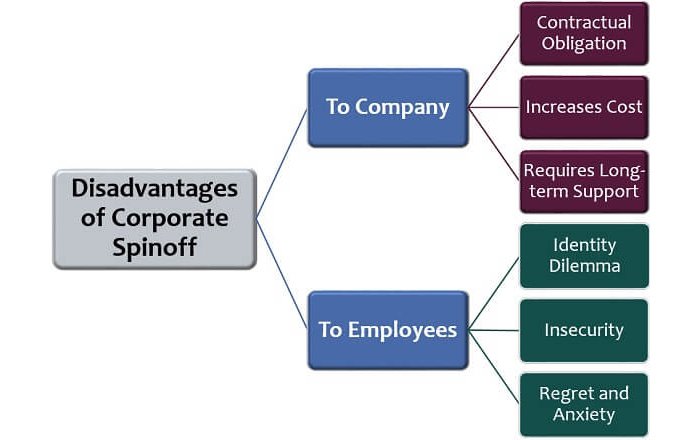
A successful spinoff solution requires meticulous separation and transition planning. Challenges with these processes may include needing to restructure human resources, develop IT systems, hand off legal responsibilities to different entities and make changes in financial reporting standards.
Added complexity can come from existing contractual arrangements across enterprise divisions that bind the parent company to its divisional businesses after a spinoff.
Effective management teams should be able to identify separating assets or liabilities as well as any skeletons hidden away in their corporate closets prior to a spin-off.
Evaluating potential drawbacks of spinoff strategies
Evaluating the potential drawbacks of spinoff strategies requires careful consideration, as there are a number of risks and challenges that need to be taken into account.
Splitting an established business can cause disruptions in its operations and lead to unfamiliar management structures, deficiencies in communication and coordination, legal complications, potential expense overruns, etc.
Moreover, due to insufficient preparation for the execution or poor implementation afterwards there is a chance of creating unrest in the workforce instead of fostering new business opportunities. Appropriate investments need to be made by executives so as to maximize their chances for success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, spinoff strategies can provide companies with many benefits by creating corporate entities better tailored to specific business goals.
Nevertheless, it is important to understand the complexity behind successful spinoff execution and implementation as well as potential risks that may occur.
Therefore, effective research and planning are needed in order to ensure smooth transition throughout the entire process. As businesses take advantage of opportunities presented by the global landscape, they should explore spinoffs as an innovative strategy for organizational growth.
After reviewing this guide on spinoffs, we hope readers feel empowered and confident to evaluate these strategic alternatives for their organizations with success!

Ryan Nead is a Managing Director of InvestNet, LLC and it’s affiliate site Acquisition.net. Ryan provides strategic insight to the team and works together with both business buyers and sellers to work toward amicable deal outcomes. Ryan resides in Texas with his wife and three children.
